
Umbro Men's Speciali Cup Low-Top Sneakers, Grey (Nimbus Cloud/Carbon/Dark Gum Frx), 7.5 UK, Grey Nimbus Cloud Carbon Dark Gum Frx, 42 EU: Buy Online at Best Price in UAE - Amazon.ae

Pantaloncini Roma 2018 Ufficiali stagione 2017/2018 Replica Autorizzata AS Roma pantaloni da calcio calcetto con striscia nera laterale (10 anni) : Amazon.it: Moda

Joma Soccer Shoes Mundial Turf 902 White Calcetto Scarpa 40.5: Buy Online at Best Price in UAE - Amazon.ae

Unitysow Scarpe da Calcio Uomo Professionale All'aperto Sportivo Erba Scarpe da Allenamento Bambino Teenager Adulto Alte Scarpe da Calcetto 35-46,Bianco,35 EU : Amazon.it: Moda

Unitysow Scarpe da Calcio Uomo Professionale All'aperto Sportivo Erba Scarpe da Allenamento Bambino Teenager Adulto Alte Scarpe da Calcetto 35-46,Bianco,35 EU : Amazon.it: Moda

adidas Hat Pure.4 Tf, Men's Trainers, Core Black Zero Met Team Shock Pink 2 : Amazon.com.be: Fashion

PUMA Men's Spirit Indoor Iii Turf Training Cross-Trainer, Shocking Orange-puma Black, 9 US : Amazon.sg: Fashion

Scarpe da Calcio FG/AG Bambino e Ragazzi TF Scarpe da Allenamento Uomo Outdoor&Indoor Scarpe da Calcetto Unisex Bambini Grigio FG 29EU : Amazon.it: Moda
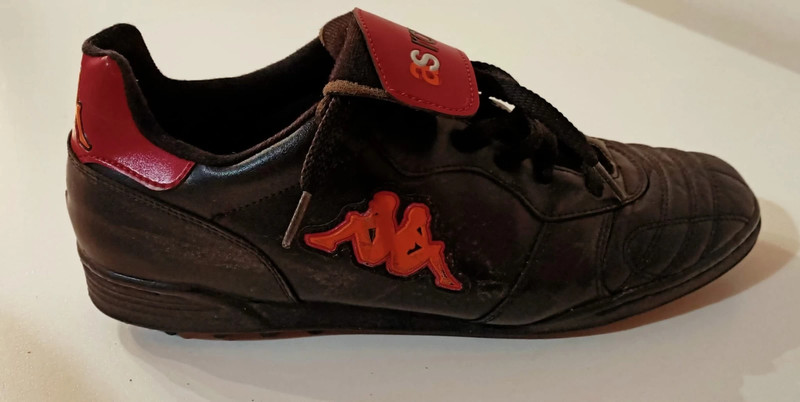
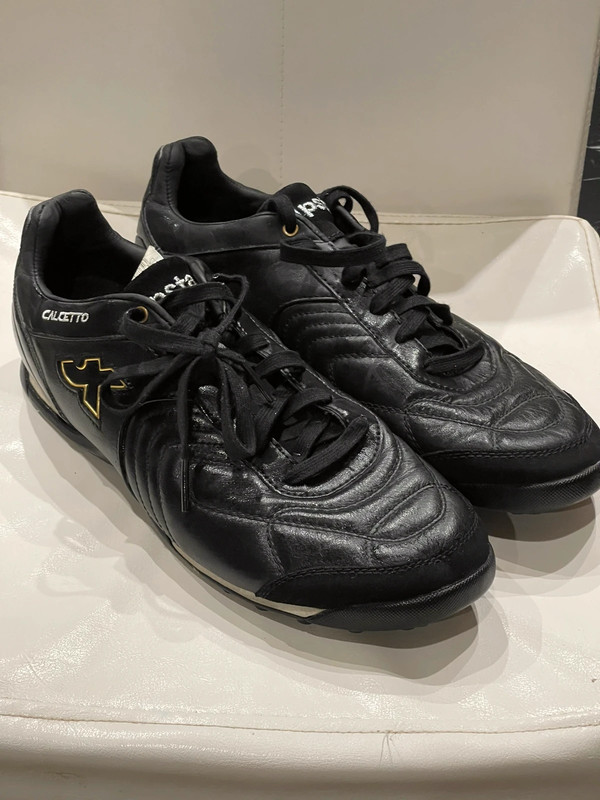















![Amazon.co.jp: [プーマ] ユニセックス・アダルト Roma Basic Inf カラー: ブラック : ファッション Amazon.co.jp: [プーマ] ユニセックス・アダルト Roma Basic Inf カラー: ブラック : ファッション](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/81JZ5E5LgdL._AC_SX675_.jpg)
